ROTATOR CUFF TEARS
WHAT IS A ROTATOR CUFF?The rotator cuff comprises 4 important muscles deep inside the shoulder. These 4 muscles are called subscapularis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus and teres minor. They all originate on the scapula (shoulder blade at the back of the shoulder) and attach via their tendons onto the humerus, close to the shoulder joint. The subscapularis is at the front, the supraspinatus is at the top and the infraspinatus and teres minor are at the back. They are important for centering the head of the humerus (the ball) in the middle of the relatively flat, small socket of the shoulder (the glenoid). They also initiate shoulder movement and control rotation. Rotator cuff tears of the shoulder are one of the most common causes of shoulder pain in patients over fifty years of age although they can occur in younger patients.
The most commonly torn tendon is the supraspinatus tendon at the top of the shoulder which runs under the shoulder tip. The tear may occur acutely caused by an injury or may occur over time (chronic or degenerative) as the tissue becomes thinner with age. The tendons must work hard throughout life and they have a relatively poor blood supply in everyone. This means if they become damaged, they can be slow to heal and a vicious cycle of damage, failure to heal properly followed by further damage, can commence. However, not all patients with a rotator cuff tear will necessarily have symptoms from it, as their shoulder can compensate by strengthening the remaining muscles and tendons. Rotator cuff tears can be further divided by whether they are partial or full thickness and also by the size of the tear. 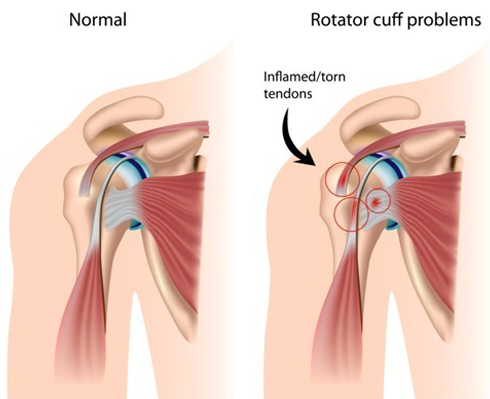 Rotator Cuff problems in the shoulder
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS?Pain is the most common symptom and this is generally felt deep inside the shoulder and on attempted movement particularly the more the shoulder is moved out to the side. Pain at night disturbing sleep is also common particularly when rolling over onto the problematic shoulder. Patients often experience weakness in the shoulder since due to the tear, there is a loss of effective muscle power available. The amount of weakness is very variable depending on the size of the tear and since other muscles can compensate.
HOW DO I KNOW IF THERE IS A TEAR?
A detailed history and examination will take place in the clinic. There are many clinical examination tests for the different rotator cuff muscles and they are used to help determine whether any are torn. An X-ray may be requested to see if there is any other cause for the pain but the tendon is most usefully assessed by an ultrasound or MRI scan.
An ultrasound scan is a dynamic scan which means the probe is moved over the shoulder by a sonographer or radiologist and the joint can be moved during the scan to help interpret the findings.
An MRI is a detailed magnetic scan (no X-rays) which can help give information about the quality of the tendon and the degree of damage to the area. MRI scans are in high demand so usually there is a long wait for it to be performed and they don't always give better information than an ultrasound. You need to lie flat and stay still for an MRI scan and they can be noisy and claustrophobic.
HOW CAN THE TEAR BE TREATED?
The treatment will begin with simple measures first since these may be successful in reducing symptoms and reinstating good function. Analgesia (pain killers) and physiotherapy to strengthen the remaining tendons and muscles can be extremely effective. Steroid injection to improve pain from secondary bursitis may be offered, however a steroid injection should be considered cautiously if there is a thought that the tendon might be surgically repaired eventually. Steroid can weaken tissue over time which would make future surgery less likely to be successful.
You may be offered surgery to repair the torn tendon(s) and this will be performed arthroscopically (keyhole). Most commonly it is performed as a day-case operation under general anaesthetic. Your anaesthetist may also perform a ‘block’ whereby local anaesthetic is injected near the base of the neck so that when you wake up after surgery the arm is very comfortable. The camera is introduced into the joint through the back of the shoulder and a general examination of the inside of the joint is performed. Sometimes, this is the first time other problems in the shoulder are discovered. They may be dealt with during that surgery. The torn tendon is assessed as to its suitability for repair. If the tendon is repairable, anchors (small bone screws) are used to gain some purchase on the humerus. Out of the anchor comes a suture (stitch) and that is threaded through the tendon so that the tendon is brought back onto the bone. The suture is tied down onto the tendon to hold it in place. Several anchors may be used depending on the size of the tear. If the tendon is of very poor quality or the tear is very large, it may not be repairable. In this case the torn tendon will be cleaned up (debrided) to remove frayed and damaged tissue. In some cases the tendon is partially, but not completely, repairable in which case that would be performed. A procedure may need to be performed on your biceps tendon which crosses the upper part of the shoulder joint. This would likley be in the form of a tenotomy or a tenodesis, please see the page on the biceps tendon. After surgery, rehabilitation can commence to strengthen the other muscles to encourage compensation for the torn rotator cuff.
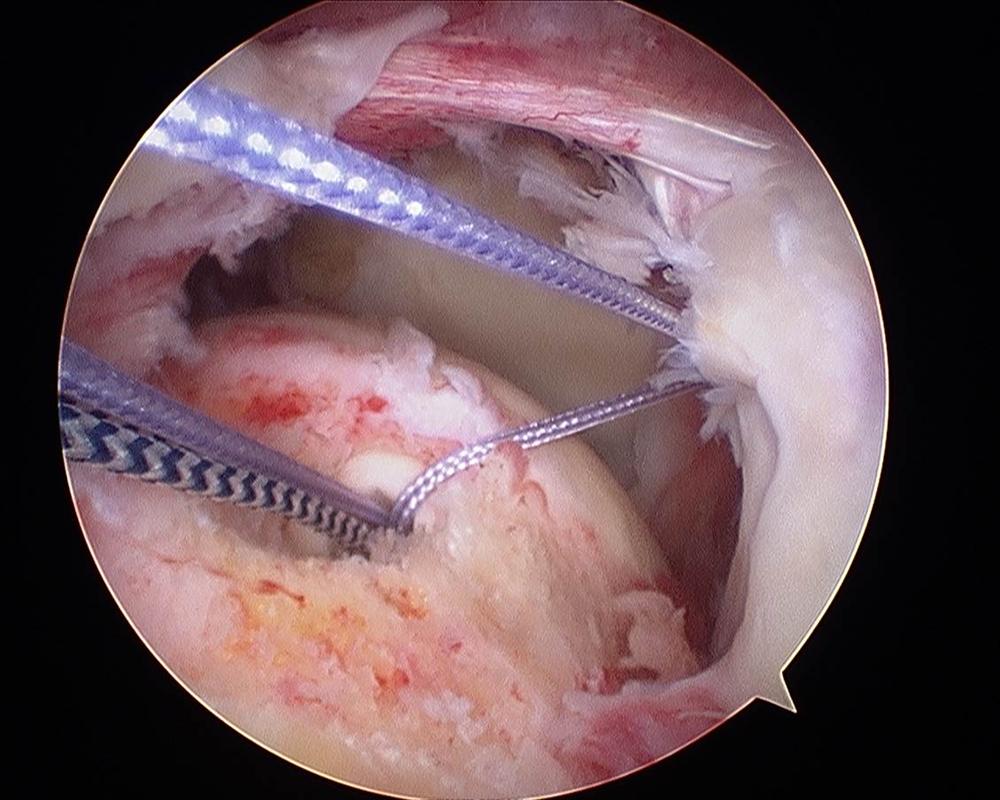
Rotator cuff repair as viewed from the lateral portal
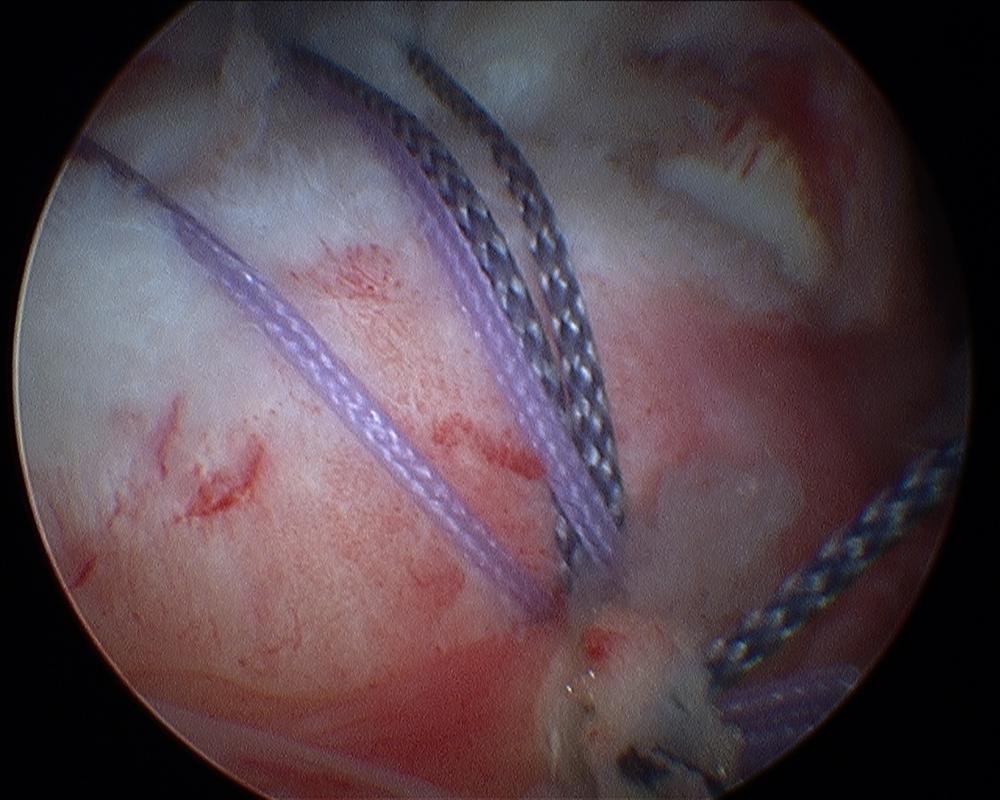
Rotator cuff repair lateral anchor (second row repair)
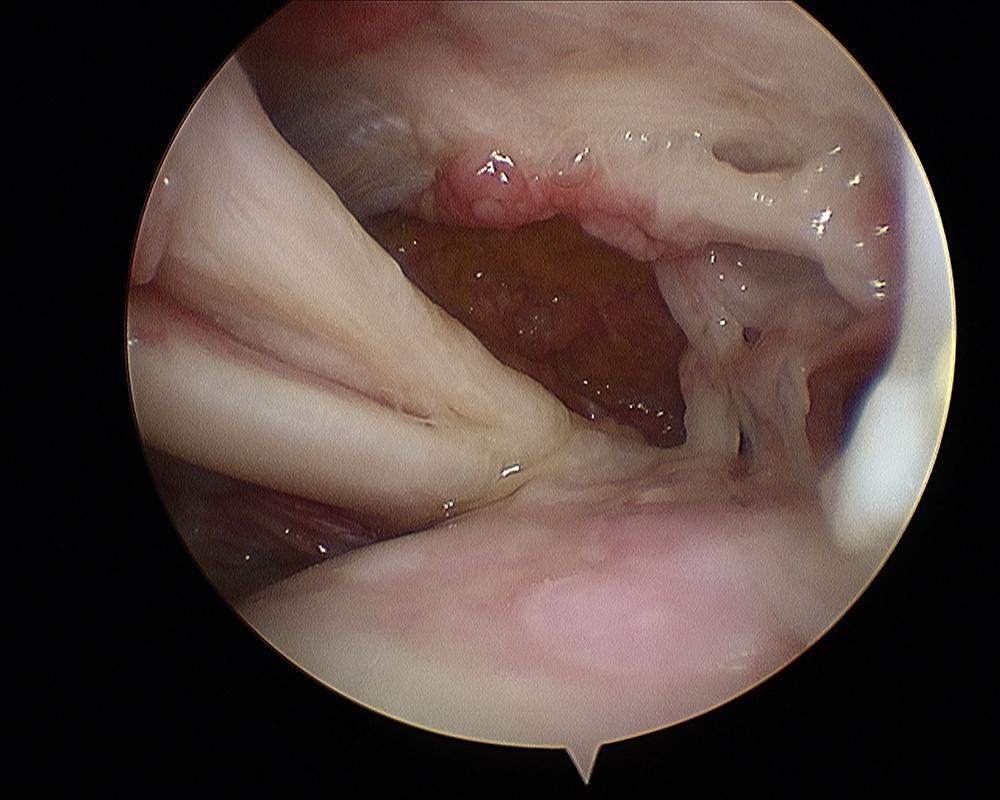
Massive (irreparable) rotator cuff tear with subluxed biceps tendon and arthritic gleno-humeral joint)
REHABILITATIONAfter the surgery you will be provided with a sling to rest your shoulder. This can be removed for washing and dressing but worn at other times including in bed at night. Whilst it is important to start moving your shoulder to prevent stiffness and to strengthen your muscle, the repair needs to be protected and allowed to heal before being loaded. You will be given detailed instructions on what you are and are not allowed to do after your surgery by myself and the physiotherapy specialists. You can expect to be in sling for approximately 6 weeks before moving the shoulder very much. Recovery from the surgery will take at least 3-6 months and some patients may take a year.
WHAT HAPPENS IF I CAN'T OR DON'T WISH TO HAVE SURGERY ?There is a very specific type of physiotherapy called ‘the anterior deltoid retraining programme’. This should be taught by a physiotherapist experienced in teaching the programme. Essentially it is a scheme of exercises to specifically train the anterior part of the deltoid muscle to perform part of the rotator cuff’s function. It can have good results and you will be offered this if it is thought to be appropriate for you. The eventual outcome of large irreparable rotator cuff tears is highly variable. Some patients’ pain settles to a manageable level although movement over-head height is likely to always be difficult. A small proportion of patients will progress on to arthritis in the joint because the muscle control has been lost. This situation is called 'rotator cuff arthropathy'. If the pain becomes unmanageable because of the arthritis, a shoulder replacement can be performed to relieve the pain (see reverse shoulder arthroplasty).
Spire Elland HospitalElland Lane
Elland
HX5 9EB
For an appointment, telephone:
Clinic bookings on 01422 324 069
Self pay enquiries on 01422 229 597
Main Hospital on 01422 229 632
BMI The Huddersfield Hospital
Birkby Hall Road
Huddersfield
West Yorkshire
HD2 2BL
Reception: 01484 533 131
Department of Orthopaedics & Trauma
Calderdale and Huddersfield NHS Foundation Trust
Huddersfield Royal Infirmary
Acre Street
Lindley
Huddersfield
HD3 3EA
NHS Secretary:
Mrs Margaret Thomas
Tel 01484 342 343
NHS Clinics Trauma:
Calderdale Royal Hospital (Halifax) and
Huddersfield Royal Infirmary
Elective Shoulder and Elbow problems:
Friday morning at Calderdale Royal Hospital, Halifax
|